Measurement
Measurement of frequency can be done in the following ways,
Countingedit
Calculating the frequency of a repeating event is accomplished by counting the number of times that event occurs within a specific time period, then dividing the count by the length of the time period. For example, if 71 events occur within 15 seconds the frequency is:
If the number of counts is not very large, it is more accurate to measure the time interval for a predetermined number of occurrences, rather than the number of occurrences within a specified time. The latter method introduces a random error into the count of between zero and one count, so on average half a count. This is called gating error and causes an average error in the calculated frequency of , or a fractional error of where is the timing interval and is the measured frequency. This error decreases with frequency, so it is generally a problem at low frequencies where the number of counts N is small.
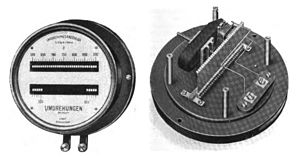
Stroboscopeedit
An older method of measuring the frequency of rotating or vibrating objects is to use a stroboscope. This is an intense repetitively flashing light (strobe light) whose frequency can be adjusted with a calibrated timing circuit. The strobe light is pointed at the rotating object and the frequency adjusted up and down. When the frequency of the strobe equals the frequency of the rotating or vibrating object, the object completes one cycle of oscillation and returns to its original position between the flashes of light, so when illuminated by the strobe the object appears stationary. Then the frequency can be read from the calibrated readout on the stroboscope. A downside of this method is that an object rotating at an integral multiple of the strobing frequency will also appear stationary.
Frequency counteredit
Higher frequencies are usually measured with a frequency counter. This is an electronic instrument which measures the frequency of an applied repetitive electronic signal and displays the result in hertz on a digital display. It uses digital logic to count the number of cycles during a time interval established by a precision quartz time base. Cyclic processes that are not electrical, such as the rotation rate of a shaft, mechanical vibrations, or sound waves, can be converted to a repetitive electronic signal by transducers and the signal applied to a frequency counter. As of 2018, frequency counters can cover the range up to about 100 GHz. This represents the limit of direct counting methods; frequencies above this must be measured by indirect methods.
Heterodyne methodsedit
Above the range of frequency counters, frequencies of electromagnetic signals are often measured indirectly utilizing heterodyning (frequency conversion). A reference signal of a known frequency near the unknown frequency is mixed with the unknown frequency in a nonlinear mixing device such as a diode. This creates a heterodyne or "beat" signal at the difference between the two frequencies. If the two signals are close together in frequency the heterodyne is low enough to be measured by a frequency counter. This process only measures the difference between the unknown frequency and the reference frequency. To reach higher frequencies, several stages of heterodyning can be used. Current research is extending this method to infrared and light frequencies (optical heterodyne detection).





Comments
Post a Comment